Schizophrenia is a chronic and severe mental health disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. It is characterized by episodes of psychosis, which can include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking, and impaired functioning. This disorder presents significant challenges not only for those diagnosed but also for their families and caregivers. In the UK, USA, and Canada, schizophrenia affects a substantial portion of the population, necessitating comprehensive strategies to manage the disorder effectively. This essay explores the challenges of living with schizophrenia and offers coping strategies, with a particular focus on its prevalence and management in the UK, USA, and Canada.
Understanding Schizophrenia
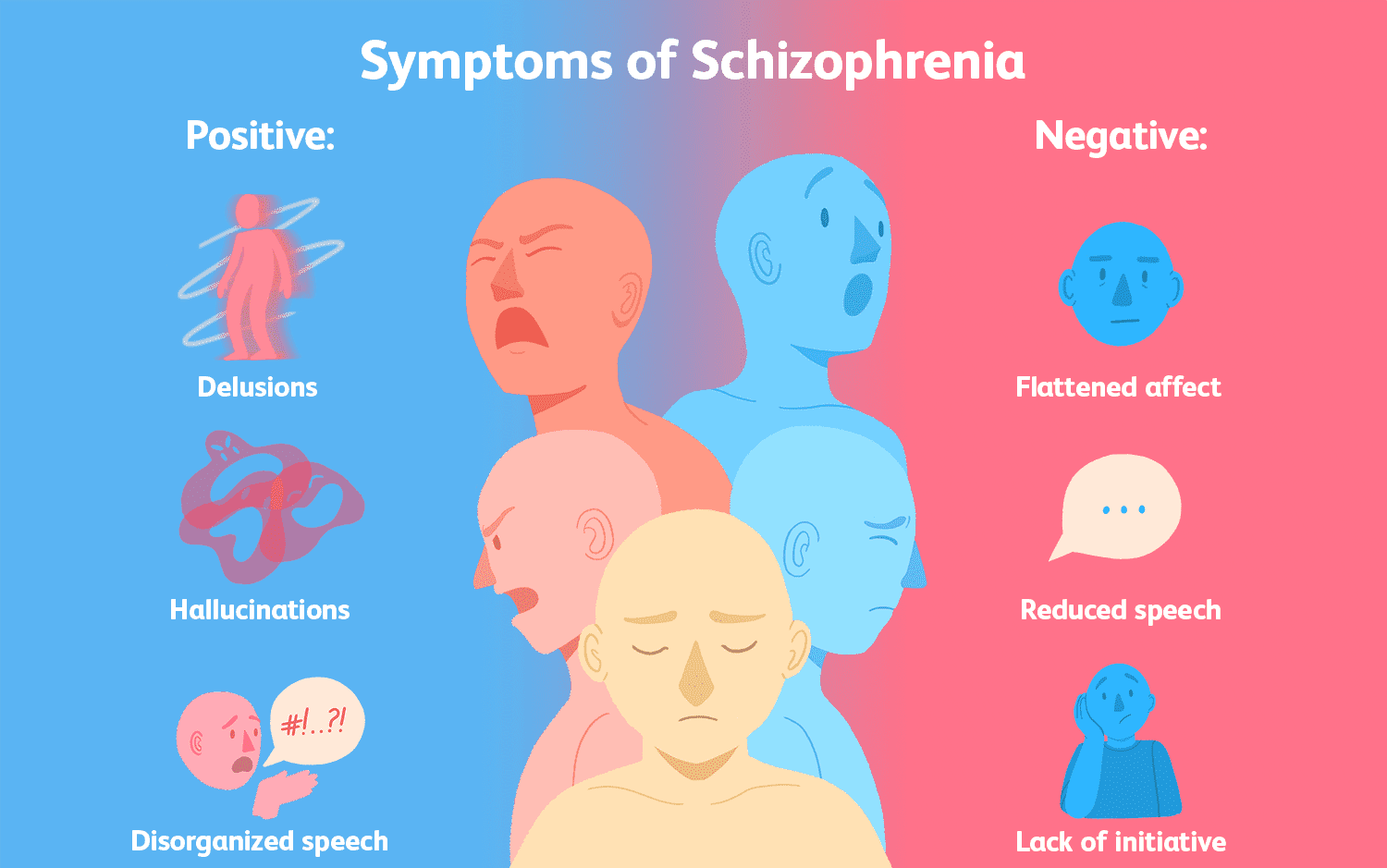
Schizophrenia typically manifests in late adolescence or early adulthood and is marked by episodes of psychosis. The symptoms are generally divided into positive symptoms (e.g., hallucinations, delusions), negative symptoms (e.g., lack of motivation, social withdrawal), and cognitive symptoms (e.g., impaired memory, difficulty concentrating). The exact cause of schizophrenia is unknown, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, biological, and environmental factors.
Prevalence in the UK, USA, and Canada
United Kingdom
In the UK, schizophrenia affects about 1 in 100 people at some point in their lives. According to the National Health Service (NHS), approximately 220,000 people are diagnosed with schizophrenia each year. The condition is a major public health issue, contributing to significant healthcare costs and social burden. The NHS provides comprehensive care and treatment plans, including medication, psychological therapies, and community support services.
United States
In the USA, schizophrenia affects about 1.1% of the population, equating to around 3.5 million people. The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) reports that the disorder often leads to significant disability and diminished quality of life. Schizophrenia accounts for a substantial portion of mental health-related hospitalizations and imposes a heavy economic burden due to healthcare costs, lost productivity, and social services.
Canada
In Canada, schizophrenia affects about 1% of the population, similar to prevalence rates in other developed countries. According to the Schizophrenia Society of Canada, approximately 330,000 Canadians are living with schizophrenia. The Canadian healthcare system offers various services to support individuals with schizophrenia, including medication, psychotherapy, and community-based programs.
Challenges of Living with Schizophrenia
Living with schizophrenia involves multiple challenges that affect various aspects of life, including personal relationships, employment, and overall well-being. These challenges are often exacerbated by societal stigma and a lack of understanding about the disorder.
Stigma and Discrimination
One of the most significant challenges faced by individuals with schizophrenia is the stigma associated with the disorder. Misconceptions and negative stereotypes can lead to discrimination in various settings, including the workplace, healthcare, and social interactions. This stigma can prevent individuals from seeking help and can worsen their condition due to social isolation and reduced self-esteem.
Symptom Management
Managing the symptoms of schizophrenia can be particularly challenging. Positive symptoms like hallucinations and delusions can be distressing and disrupt daily life. Negative symptoms, such as anhedonia (inability to feel pleasure) and social withdrawal, can lead to a diminished quality of life and difficulties in maintaining relationships and employment. Cognitive symptoms can impair daily functioning and make tasks like managing finances or adhering to treatment plans difficult.
Medication Side Effects
While antipsychotic medications are essential for managing schizophrenia, they can have significant side effects, including weight gain, drowsiness, and metabolic issues. These side effects can deter individuals from adhering to their medication regimen, leading to relapse and worsening of symptoms.
Access to Care
Access to comprehensive care can be inconsistent, particularly in rural or underserved areas. Even in countries with robust healthcare systems, there can be barriers to accessing specialized mental health services, leading to delays in diagnosis and treatment.
Coping Strategies
Effective management of schizophrenia involves a combination of medical treatment, psychological support, and lifestyle adjustments. Here are some key strategies for coping with the disorder:
Medication Adherence
Adhering to prescribed medication is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing relapse. Working closely with a healthcare provider to find the right medication and dosage with manageable side effects is essential. Regular follow-up appointments can help monitor progress and make necessary adjustments.
Psychological Therapies
Psychological therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and family therapy, can provide valuable support. CBT can help individuals manage symptoms by addressing negative thought patterns and behaviors, while family therapy can improve communication and support within the family unit.
Support Networks
Building a strong support network is vital for individuals with schizophrenia. This network can include family, friends, healthcare providers, and support groups. Peer support groups, both in-person and online, can offer a sense of community and shared experience, which can be incredibly beneficial.
Education and Awareness
Educating oneself and others about schizophrenia can help reduce stigma and promote understanding. Advocacy and public awareness campaigns can also play a significant role in changing societal attitudes towards mental health disorders.
Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can positively impact mental health. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep can improve overall well-being and help manage symptoms. Avoiding alcohol and recreational drugs is also crucial, as these substances can exacerbate symptoms and interact negatively with medications.
Stress Management
Stress can trigger or worsen symptoms of schizophrenia. Developing effective stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga, can help individuals cope with daily stressors and reduce the risk of relapse.
Vocational Rehabilitation
Vocational rehabilitation programs can support individuals in finding and maintaining employment. These programs often provide job training, placement services, and ongoing support to help individuals succeed in the workplace.
Schizophrenia in the UK
In the UK, the NHS provides comprehensive care for individuals with schizophrenia, including access to medication, psychological therapies, and community support services. The Care Programme Approach (CPA) is a framework used to plan and coordinate care for people with severe mental health problems. It ensures that individuals receive personalized care plans and regular reviews to address their needs.
Additionally, organizations like Rethink Mental Illness and Mind offer resources, support, and advocacy for individuals with schizophrenia and their families. These organizations work to raise awareness, reduce stigma, and improve access to care.
Schizophrenia in the USA
In the USA, treatment and support for individuals with schizophrenia are provided through a combination of public and private healthcare systems. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) has expanded access to mental health services, but challenges remain, particularly for uninsured or underinsured individuals.
Organizations such as the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) provide education, advocacy, and support for individuals with schizophrenia and their families. NAMI’s programs, such as Family-to-Family and Peer-to-Peer, offer valuable resources and support networks.
Schizophrenia in Canada
Canada’s publicly funded healthcare system provides comprehensive mental health services, including treatment for schizophrenia. Provinces and territories offer various programs and services, often coordinated through community mental health centers.
The Schizophrenia Society of Canada and provincial organizations provide support, education, and advocacy for individuals with schizophrenia and their families. These organizations work to improve public understanding of schizophrenia and promote policies that enhance access to care and support services.
Conclusion
Living with schizophrenia presents significant challenges, but with the right strategies and support, individuals can manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. In the UK, USA, and Canada, substantial efforts are being made to provide comprehensive care and reduce the stigma associated with the disorder. By promoting education, advocacy, and integrated care, we can improve outcomes for individuals with schizophrenia and support their journey towards recovery.